Bates Masi + Architects have designed a single family home in East Hampton, New York.
[toggle title=»From the architects»]
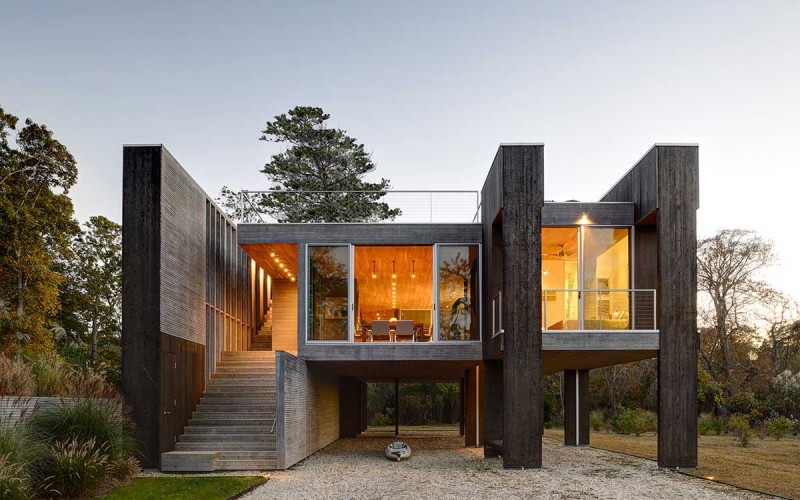
Straddling freshwater wetlands and a tidal estuary just six feet above sea level, this house’s site demands extraordinary sensitivity to environmental concerns. Local zoning restricts the structure’s maximum coverage and proximity to wetlands areas, while FEMA requirements set the first floor structure above the base flood elevation. The house’s basic massing is therefore predetermined, limited to a one story, 1,900 square foot design, raised eight feet above the ground. The spaces within this envelope are arranged, articulated, and fenestrated based on an innovative structural system that infuses the house’s inner areas with light and circulating air.
Whereas most waterfront construction uses pilings to establish an artificial ground plane upon which a conventional house is built, in this project these structural members are integral: 16 exposed, glue-laminated piles stake out the enclosing walls for each of the three bedrooms and extend continuously from the ground through the roof. The spaces between these piles house “utility” functions: closet, desk, laundry, pantry, and shower compartment. In addition to these conventional utilities, three vertical voids are opened between the piles to serve the spaces around them.
Without occupying any of the limited allowed coverage, these open areas add considerable value by improving the house’s interior environmental quality and diminishing its impact on the local environment. The benefit is threefold: each opening draws light though the interior spaces to the carport below, conducts rainwater from the roof deck to the ground via integral downspouts carved into the piles, and ventilates by siphoning air through the middle of the structure.
At the roof the projecting piles divide the space between a deck directly coinciding with the living areas below and a modular planting system installed above each bedroom to reduce runoff. The projecting piles also serve as supports for photovoltaics that power geothermal pumps, utilizing the abundance of high ground water to heat and cool the house. At the ground level, the space below the house is utilized for parking and storage to minimize the footprint on the site.
By allowing voids to permeate through the house, the owners have multiple visual connections to the landscape from below, within and above the house, encouraging a sense of place.
…[/toggle][toggle title=»От архитекторов»].
Трансграничным пресноводные водно-болотных угодий и приливную лиман всего шесть футов над уровнем моря, сайт этот дом в требует внеочередного чувствительность к экологическим проблемам. Местное зонирование ограничивает максимальный охват структура, и близость к водно-болотным угодьям районах, в то время как требования FEMA установить первую конструкцию пола над базой наводнений высоте. Основной массирование дома является поэтому предопределено, ограничивается одной истории, 1900 квадратный дизайн нога, поднял восемь футов над землей. Пространства внутри этой оболочки расположены, сформулированы, и Фенестрированные основана на инновационной структурной системы, что вселяет внутренние районы доме с света и циркуляции воздуха.
В то время как большинство строительство набережной использует сваи установить искусственную плоскость заземления, на которой строится обычный дом, в этом проекте эти конструктивные элементы являются неотъемлемой: 16 подвергается, Клееная сваи застолбить ограждающих стен для каждой из трех спален и непрерывно продолжаются от земли через крышу. Промежутки между этими свай дома функций «полезности»: шкаф, стол, прачечная, кладовая, и душ отсек. В дополнение к этим обычных утилит, три вертикальные пустоты открыт между свай, чтобы служить пространства вокруг них.
Без занимая какой-либо из ограниченного позволило покрытия, эти открытые участки добавить значительную ценность путем улучшения интерьера качества окружающей среды в доме и уменьшая его влияние на местную окружающую среду. Выгода состоит из трех частей: каждое отверстие привлекает свет, хотя внутренние помещения к ниже навес, проводит дождевую воду от крыши до земли через интегральных водосточных труб, вырезанных в груды, и вентиляцию с помощью сифона воздух через середину структуры.
На крыше выступающие сваи делят пространство между палубы непосредственно совпадающие с жилых помещений и ниже модульной системы посадки, установленной над каждой спальне, чтобы уменьшить сток. Выступающие сваи также служить в качестве опоры для фотовольтаики, что власть геотермальные насосы, используя обилие высоких грунтовых вод для обогрева и охлаждения дома. На уровне земли, пространство под домом используется для парковки и хранения, чтобы свести к минимуму след на месте.
Позволяя пустоты проникать через дом, владельцы несколько визуальных соединения с ландшафтом снизу, в пределах и выше дома, поощряя чувство места.
..[/toggle]
About Author
Write a Comment
Only registered users can comment.